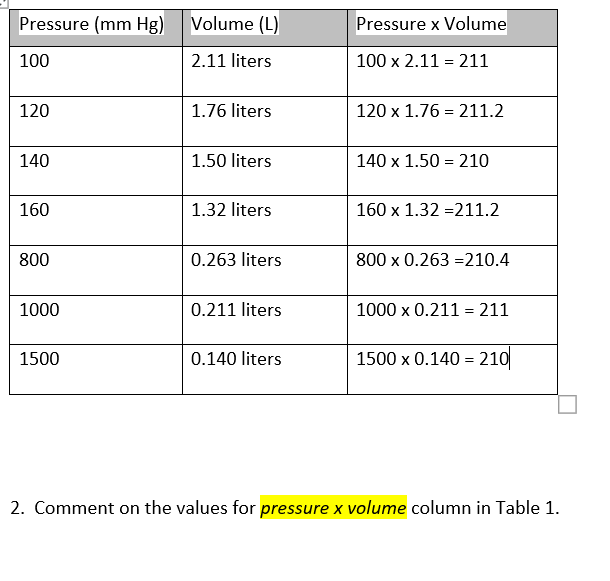
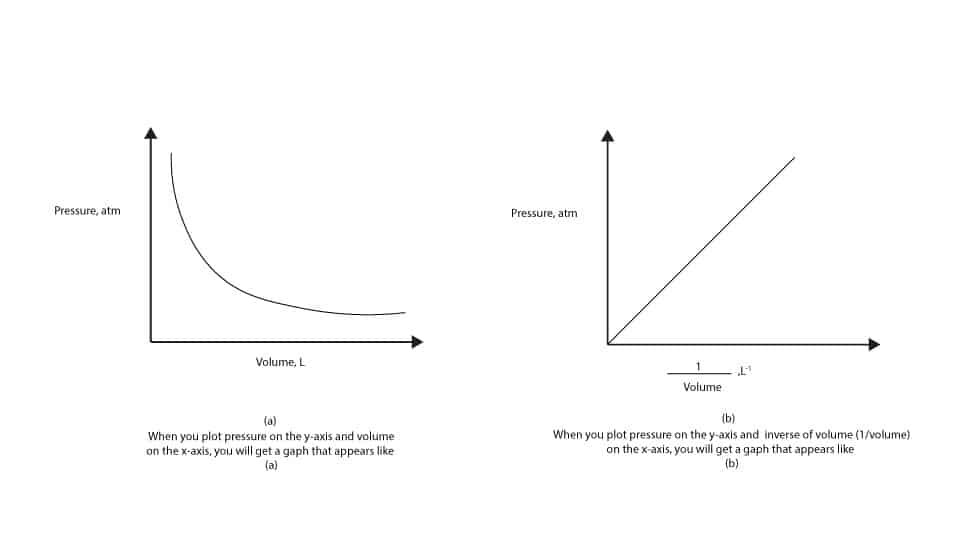
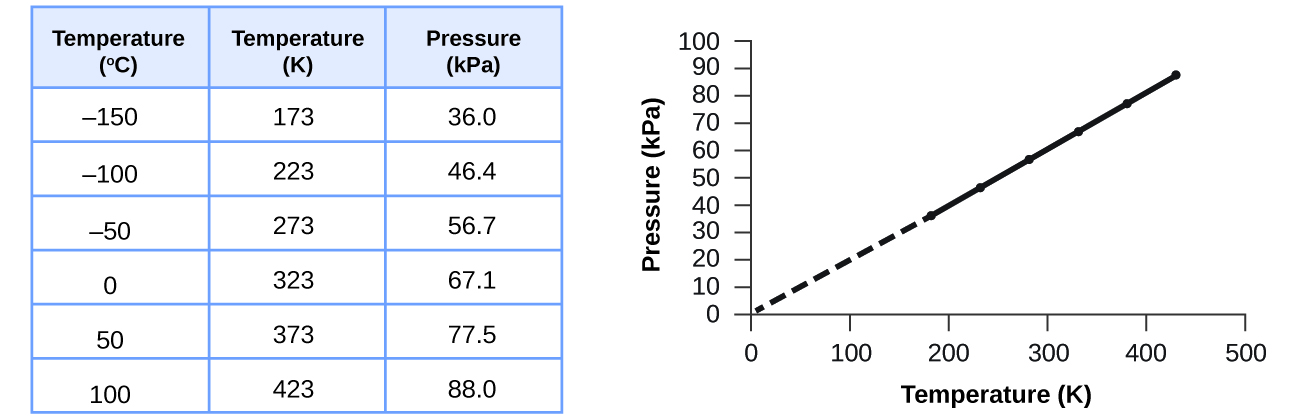
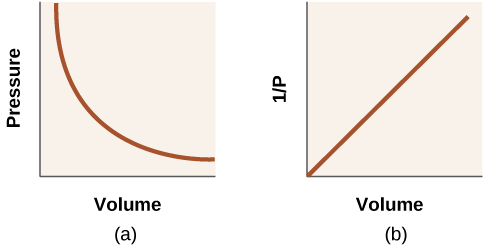
SOLVED: Which graph shows the correct relationship between pressure and volume of an ideal gas at a constant temperature? Hint: The graphs are plotting P on the y-axis and V on the

When Does the Kinetic Theory of Gases Fail? Examining its Postulates with Assistance from Simple Linear Regression in R | The Chemical Statistician

In Boyle's Law, when we plotted the graph between volume and pressure, why we put the volume in the x -axis and pressure on Y-axis?

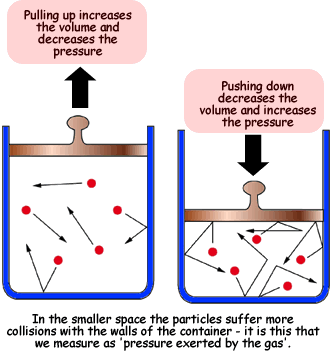
Pressure Volume & Temperature. In liquids and solids, the primary particles (atoms or molecules) are always in contact with each other. In gases, particles. - ppt download

PPT - Gases – Kinetic Theory revisited (assumptions for “ Ideal” Gases) PowerPoint Presentation - ID:4342875
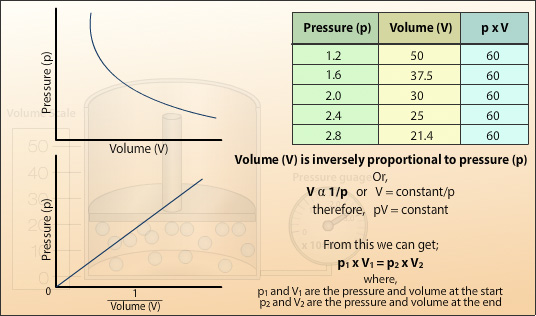
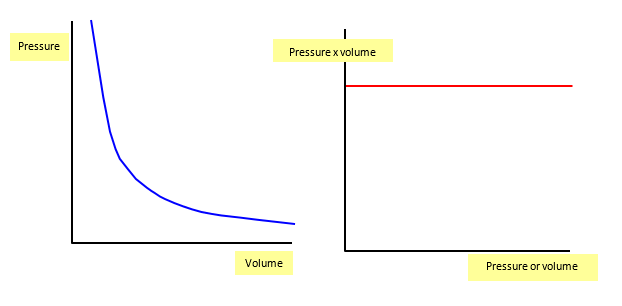
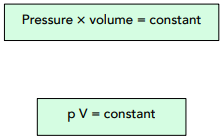
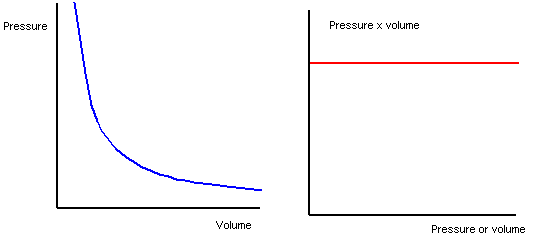
Pressure and volume relationship of a gas – Boyle's law - Pass My Exams: Easy exam revision notes for GSCE Physics
Solved: Pressure-Volume Relationship GASES Plot the volume against the pressure below, with volume [Physics]

How to Calculate the Pressure of a Gas Based on the Observed Volume Change from Known Work Done | Physics | Study.com

Partial pressure of gas = total pressure x volume % How - Chemistry - Solutions - 14648991 | Meritnation.com

Examples from original pressure-volume loops (x-axis: volume in ml,... | Download Scientific Diagram